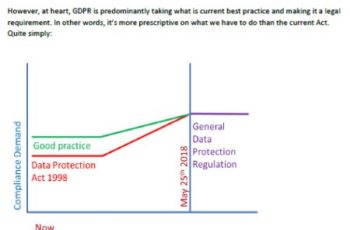
GDPR stands for General Data Protection Regulation. GDPR is the new legal framework from the EU which aims to ensure digital privacy and protection of personal data. The GDPR mandates that all data controllers must implement appropriate and relevant technical and organisational measures that provide compliance with GDPR.
This article provides guidance and direction for businesses and organisations to draft a GDPR policy based on the GDPR framework.
Contents
GDPR Policy for Small Businesses
Policy Statement






- The management of the company ensures personal data protection and privacy and ensures compliance with GDPR.
- The GDPR policy of this company applies to all company’s data processing functions on employee data, client data, customer data and any third party contractor data.
- The company appoints a specific owner Mr X who is responsible for ensuring all GDPR related compliance and performing reviews for any changes or updates.
- The company can take any disciplinary action including reporting a criminal offence in case there is a data breach.
- All employees, partners, owners and third party agents are expected to have read, understood and complied with the GDPR policy.
Most of the sections are covered in the data privacy policy and the data protection policies mentioned before. A company can customise based on its specific requirements.
GDPR Policy Template for Charities


This document aims to provide a practical and concise template for a working Data Protection policy. The trustees of small charities or the board members can use this template and craft a compliant GDPR policy for their charities.
Lawful Data Collection
In this section, the charity should show procedures for lawful data collection. Lawful data collection means that the charity is collecting the personal data of employees or contributors with consent and in a transparent manner.
- The charity maintains a transparent Data Registration System to ensure all data is collected fairly.
- The charity declares that it collects personal information of the following category of individuals: Volunteers, Employees, External Consultants and Contributors.
- The charity ensures that all personal data is collected only after individual consent and for legitimate reasons.
- The charity ensures that proper awareness regarding data collection and its purpose is maintained.
Lawful Data Processing and Disclosure
This section covers the charity’s responsibilities when it comes to lawful, fair and transparent data processing. This section includes the ways in which charity processes as well as uses various personal information.
- The charity would control and process data such as Name, Contact Information and other personal information.
- The charity would process and use this data only for legitimate communications specifically related to the campaigns and causes approved by the charity.
- The charity would process and use personal information in case it is mandatory to submit in accordance with legal or government regulation.
Security of Personal Data



This section covers the various provisions in place to protect and secure the personal data records.
- The charity ensures that it takes appropriate security measures so that no unauthorised person has access to personal records of the charity.
Information Access Requests
This section covers the charity’s guidelines in response to any personal data requests that are made by different entities.
- The charity has a dedicated person in place who is responsible for responding to all information access requests for personal data.
- The charity ensures that the responsible person identifies the nature of the requests and processes the request only after appropriate authorisation.
- The charity reserves the right to reject information access request in case the charity thinks that information release is irrelevant or unjustified.
Data Breach








This section includes provisions and compliances in case there is a data breach. Additionally, this section should also include disciplinary actions responding to the data breach.
- In case of a breach, the charity would immediately notify the concerned individuals.
- Depending on the extent of breach and possible consequences, the charity would take appropriate legal and disciplinary actions.
The charity can customise and modify the number of sections and their content based on individual requirements.
GDPR Policy Template for Schools


The schools collect and use personal information about students, teachers and staff to support educational and administrative activities. There is also be a legal government requirement to maintain student and teacher data records.
The aim of this template is to provide school authorities with actionable guidelines on drafting a GDPR policy for their schools. The school authorities act as data controller with personal information about teachers and students. Hence it is necessary to create a policy which is in compliance with the GDPR framework that ensures all personal data is treated safely and fairly.
The school should declare and comply with the data protection principles of GDPR. Listed below are some other sections that a GDPR policy for schools should include.
Information Collection
This section includes information about the various type of data that the school collects for each student, teacher and other administrative staff. The school should also declare the purpose of data collection which is to support learning and monitor progress.
- The school reserves the right to collect the student’s personal information such as full name, parent contact information, address, ethnicity, religion, gender, nationality and birth date.
- The school reserves the right to collect, store and maintain the student’s academic information such as attendance, grades and class behaviour.
- The school reserves the right to collects information such as student medical history and previous school records.
- The school reserves the right to collects teacher’s personal information such as name, contact information, address, gender, nationality, birth date and religion.
- The school reserves the right to collect academic and professional information of teachers such as their educational background, years of work experience, past employer details and areas of expertise.





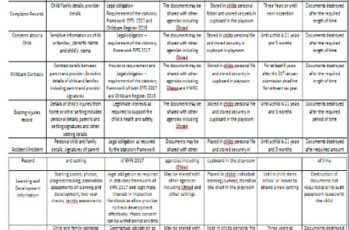




Information Storage and Access
This section should provide information on the storage of the collected data and the provisions in place to access that data. The schools should declare any unauthorised access to student or teacher data as illegal.
- The school uses a Data Management software to store all the data and ensures that it preserves the integrity and confidentiality of the data.
- The school shares the data only with student alumni, the state and national government and department of education. No data is shared without permission from the concerned individuals.
- The student and teachers of the school are allowed to access their data and make any updates if necessary.
Information Breach
This section should include provisions in case there is a data breach or data theft. As a data controller, the school is responsible and hence there should be proper guidelines for prevention of breach as well as disciplinary measures.
- The school ensures that the personal records of students and teachers are both physically and electronically protected from illegal attempts of theft and hacking.
- In case of a breach, the school is responsible for informing the concerned students, parents and teachers and take further corrective actions.
The sections above are some excellent examples of what to include in a Data Protection template. Based on individual school requirements, the sections can be customised.
GDPR Policy Template for Clubs


Purpose
Various type of clubs collect personal information for membership and marketing purposes. Hence they act as data controllers and need to comply with a data regulation and protection policy.
The aim is to provide the club owners or club board members with actionable guidelines on drafting a GDPR policy. With the help of this policy, the club owners will be able to use member personal data in a safe and fair way.
Data Collection and Usage
This section should describe all the kinds of personal information collected by clubs. The clubs should also explicitly declare the different ways in which they plan to use or share the member data.
- The club reserves the right to collect and store personal information such as name, contact information, address, employment details, salary and personal interests when someone applies for a new membership.
- The club reserves the right to use the member’s personal data to inform them about various club activities, offers and new information about the club.
- The club does not share member’s personal information to any third party sponsors or agencies.
Accountability and Consent










Under GDPR, the accountability for safe and fair use of data extends to both data controllers and data processors. The clubs should be explicit about the responsibilities of the people who manage member data. The rights of members include the right to give consent as to how the personal data is used.
- The club ensures that no third party agency or sponsor misuses member’s personal data.
- The members reserve the right to stop any use of their personal data for any club purposes. For example, members can choose to opt out from a certain club activity where their personal information is used or unsubscribe their name from club communications.
GDPR Policy Template for Websites
Many websites collect personal information. They either do it passively through cookies or actively through online forms and questionnaires. Hence they act as data controllers and it is necessary for them to have a GDPR compliance policy. This template provides a draft.

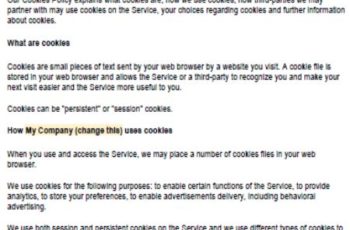
Privacy Preferences
This section should inform the website visitors about what data is being collected from them and who will access them. Additionally, the website owners should provide visitors with the necessary preference rights.
- This website uses cookies to collect information for improving the customer experience. You can opt-out of this if you want.
- The website uses following plug-ins to enhance user experience and they collect the following personal information.
- This website collects the following personal information for tracking and analytics purposes. You can opt-out of this if you want.
Some Important Definitions
Before starting with the actual guidelines, it is essential to know about some key definitions.
Personal Data:
This includes any information which can directly or indirectly identify a unique person. Examples include Name, Contact Information or any government identification number.
Data Subject:
This refers to any unique living person whose personal data is held by an organisation.
Data Controller:
This broadly refers to any entity which collects, owns, controls, manages, maintains and processes personal information of people.
Data Processor:
Sometimes, another entity might process the data on behalf of the organisation (data controller).
Since the GDPR policy is vast and covers a range of aspects, it is a good idea to divide the policy as Data Protection Policy and Data Privacy Policy.
GDPR Data Protection Policy


This aspect of the policy primarily deals with the safeguarding of the data from theft or vulnerabilities.
Data Integrity
The data controller should ensure that all personal data is kept accurate and up to date. This section should include guidelines on how the organisation needs to make the necessary reviews, updates and changes to protect the data integrity.
- The company ensures that all personal data is reviewed regularly to check for updates. Out of date data should be deleted from the system without delay.
- The company is responsible for implementing all procedures that ensure accurate data is present in the system at all times.
Data Security Mechanisms
A lot of times data controllers collect sensitive personal information from individuals. In such cases, it is necessary that the data is protected from theft or vulnerabilities. In this section, the organisation should define guidelines that show the provisions in place to protect sensitive data.
- The company ensures that it uses encryption and other techniques to prevent sensitive and personal data from malicious attacks.
- The company provides password protection, antivirus software, firewalls, network security and other measures to protect personal data.
- The company provides physical protection, remote data storage as well as periodic data backups to protect personal and sensitive data.
GDPR Data Privacy Policy
This aspect of the policy primarily deals with controlling data access. It mainly deals with managing who is authorised to access what kind of data.
Data Collection
The data controller should ensure that it collects any personal data only for specific, explicit and legitimate purposes. This section should provide guidelines that explain the reasons for data collection and the transparent procedure followed.
- The company uses the individual’s data only for the specific purpose as communicated to the individual before data collection.
- The company ensures that personal data collected is adequate, limited and relevant just for what is necessary for processing. This should be reflected in all data collecting procedures.
Data Processing
According to Article 5 of GDPR, all data must be processed lawfully, fairly and transparently. This section should ensure that the data controller provides a clear understanding to the data subject on how precisely the data controller uses the data.
- The company processes the following categories of data of an individual as per the lawful basis only.
- The company ensures that the data processor understands the data privacy rights of the individual and does not indulge in any unlawful data processing.
Data Subjects’ Rights
The GDPR framework ensures that data subjects have a right to know more about how the company or data controller is using their data. This section should include the privileges that the company allows the data subjects when it comes to data privacy.
- The data subjects can demand information about the exact usage of their data.
- The data subjects have a right to cancel, discontinue or opt-out their personal information from any of the data controller’s processes.
- The data subjects have a right to sue the data operator if their data is being used without their knowledge and causing them damage or distress.
Consent
The GDPR framework requires the approval of any individual before the company can collect, use or process their personal information. This section should include the exact definition of consent and what it means for individuals.
- The company defines consent as the permission which is unambiguous, explicitly and freely given by a data subject to collect or process their personal data.
Data collection via forms
A lot of companies collect personal information via forms. As per GDPR laws, it is necessary to inform the website visitors about where this data will be used.
- The website uses the information collected via forms for marketing and product related information.
- The website ensures that your personal information is not shared with any third party agents.
The document has covered many sections on data protection and data privacy previously. Websites can use them to customise their GDPR policies.